Lesson 27 - Snap and align
Snapping is a common feature in graphics editor applications. The core idea is to automatically align element boundaries or anchor points to the nearest pixel grid lines or other graphics when moving, drawing, or scaling elements. In this lesson, we'll introduce their implementation.
Snap to pixel grid
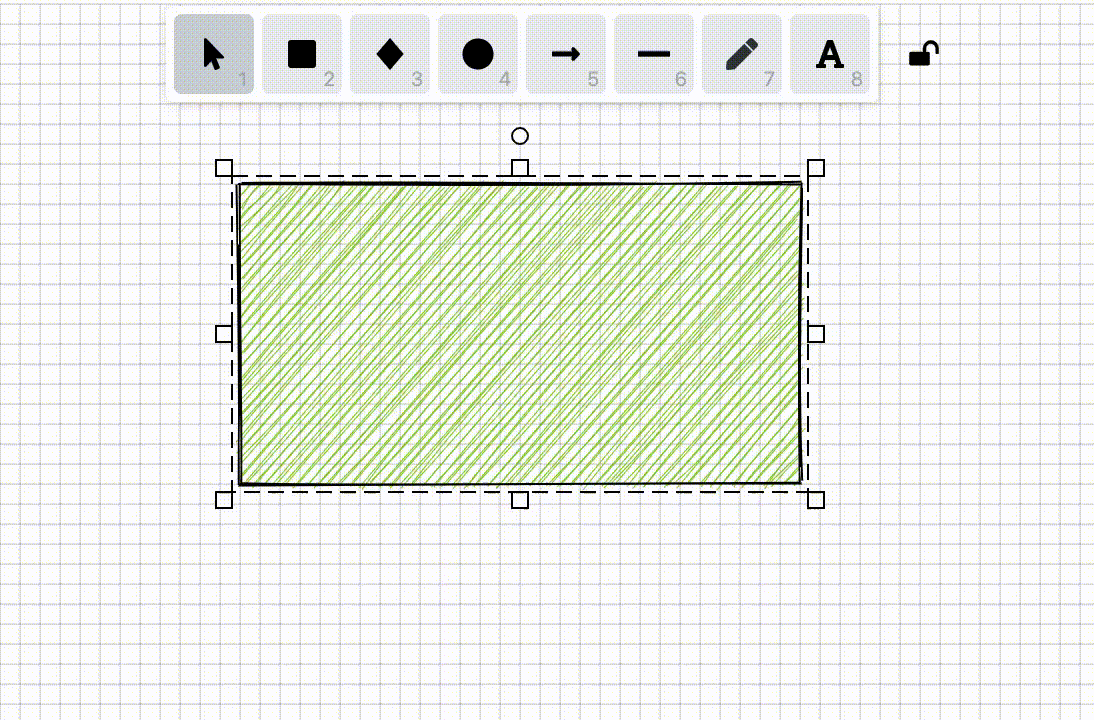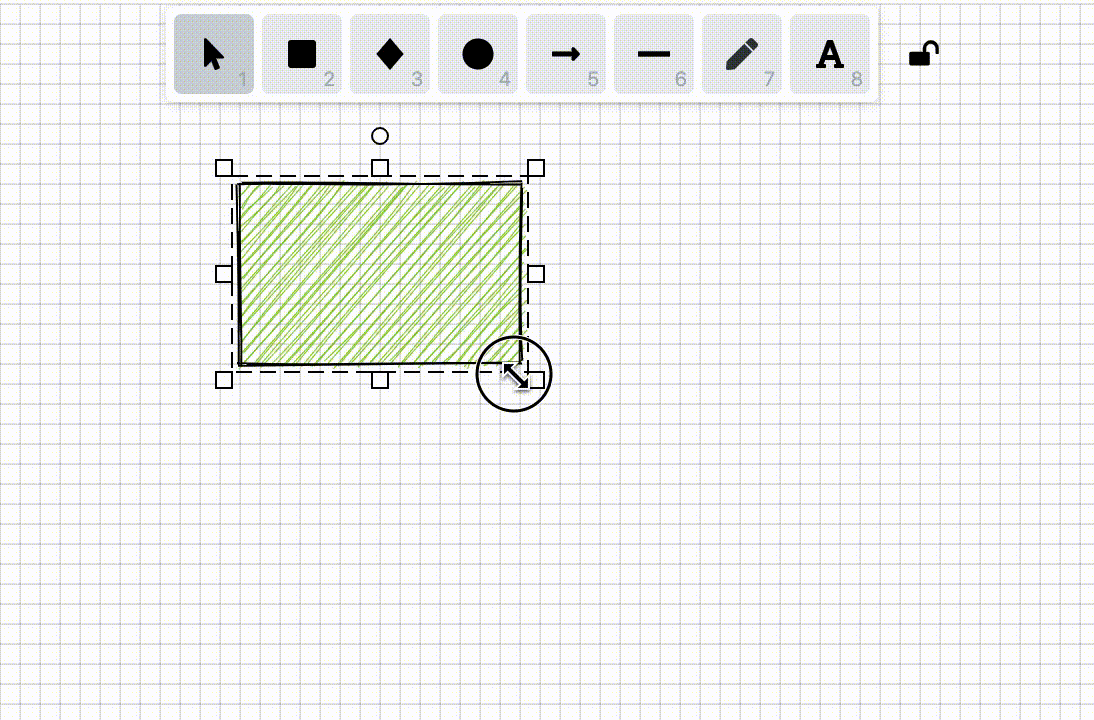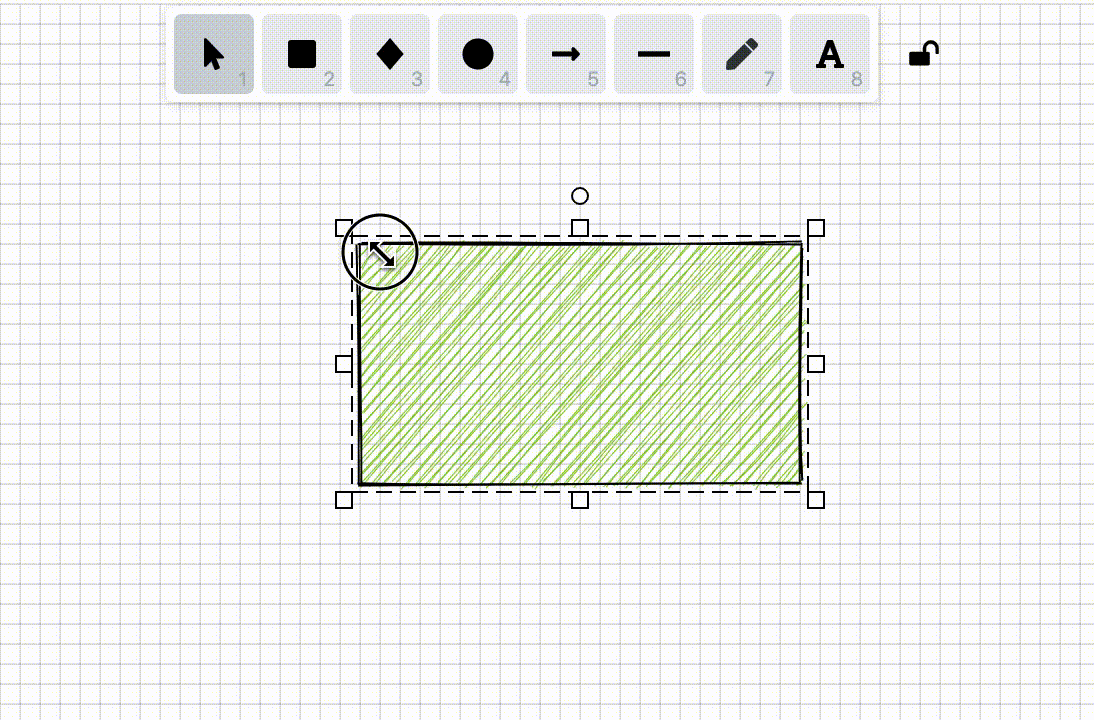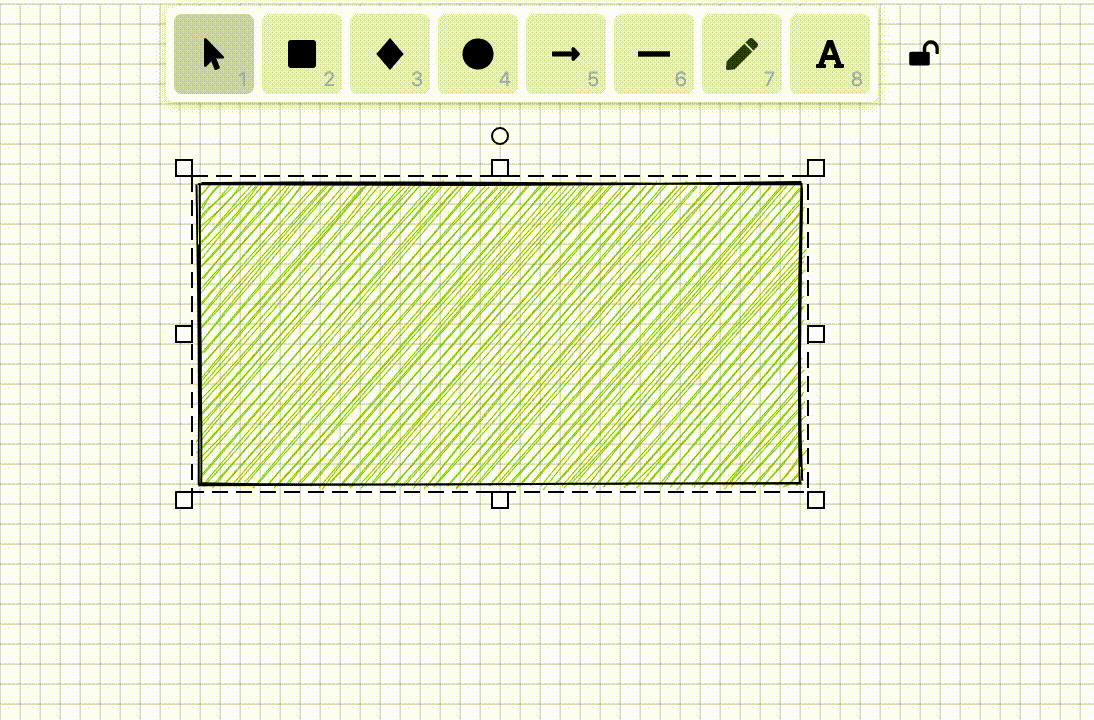
In [Lesson 5 - Drawing grids], we introduced how to efficiently draw straight-line grids. In some drag interactions such as moving and drawing, snapping to the minimum unit of the grid ensures that the position or geometric information of graphics are integers. This feature is called "Snap to pixel grid" in Figma and can be enabled in "User Preferences".
export interface AppState {
snapToPixelGridEnabled: boolean;
snapToPixelGridSize: number;
}To implement this feature, we first need to calculate the coordinates of points in the world coordinate system. When users drag, scale, or draw graphics, we get the current coordinates (such as x, y), then round these coordinates to the nearest integer (pixel point) or the specified grid spacing:
// Snap to custom grid (e.g. 10px)
function snapToGrid(value, gridSize = 10) {
return Math.round(value / gridSize) * gridSize;
}Then apply this processing function in all Systems that need to calculate coordinates of points in the world coordinate system (such as Select, DrawRect):
let { x: sx, y: sy } = api.viewport2Canvas({
x: prevX,
y: prevY,
});
let { x: ex, y: ey } = api.viewport2Canvas({
x,
y,
});
const { snapToPixelGridEnabled, snapToPixelGridSize } = api.getAppState();
if (snapToPixelGridEnabled) {
sx = snapToGrid(sx, snapToPixelGridSize);
sy = snapToGrid(sy, snapToPixelGridSize);
ex = snapToGrid(ex, snapToPixelGridSize);
ey = snapToGrid(ey, snapToPixelGridSize);
}In the example below, we set snapToPixelGridSize to 10. You can experience the effect by dragging, moving, and drawing:
Object-level snapping
The implementation of snapping functionality in Excalidraw is divided into the following key steps:
- Check if the current operation allows snapping (isSnappingEnabled).
- Calculate all snappable points and gaps (getPointSnaps).
- Real-time calculation of snap offsets and guide lines during drag/scale operations (snapDraggedElements / snapResizingElements).
- Pass snapLines to the UI layer and render guide lines on the canvas (renderSnaps).
Below, we will implement this by following the steps outlined above.
Is snapping enabled
We have added the following configuration options to the application settings, which can also be enabled in the “Preferences Menu”:
export interface AppState {
snapToObjectsEnabled: boolean;
}Triggered when dragging and moving or drawing shapes:
Get point snaps
Snap points are divided into two categories: selected shapes and other shapes. For one or more selected shapes, common snap points include the four corners and the center of the bounding box:
const { minX, minY, maxX, maxY } = api.getGeometryBounds(
elements.map((id) => api.getNodeById(id)),
);
const boundsWidth = maxX - minX;
const boundsHeight = maxY - minY;
return [
[minX, minY], // corners
[maxX, minY],
[minX, maxY],
[maxX, maxY],
[minX + boundsWidth / 2, minY + boundsHeight / 2], // center
] as [number, number][];Considering performance, we should minimize the number of times we detect the attachment points of the selected shape relative to all other shapes. We've already covered similar issues in Lesson 8 - Using spatial indexing, where we only retrieve shapes within the viewport.
const unculledAndUnselected = api
.getNodes()
.map((node) => api.getEntity(node))
.filter((entity) => !entity.has(Culled) && !entity.has(Selected));Similarly, calculate the reference points for these shapes:
const referenceSnapPoints: [number, number][] = unculledAndUnselected
.map((entity) => getElementsCorners(api, [api.getNodeByEntity(entity).id]))
.flat();Next, compare the snap points of the selected shape with those of other shapes one by one. Identify the pair of points that are closer horizontally or vertically, and record the distance difference between them as the subsequent snap distance:
nearestSnapsX.push({
type: 'point',
points: [thisSnapPoint, otherSnapPoint],
offset: offsetX,
});
minOffset[0] = Math.abs(offsetX);Once all snap points have been calculated, this minimum distance can be used as the snap distance. It is important to note that the graph has not yet moved according to the snap distance at this stage. Therefore, we need to assume the graph has already moved to its final position and perform another round of calculations:
// 1st round
getPointSnaps();
const snapOffset: [number, number] = [
nearestSnapsX[0]?.offset ?? 0,
nearestSnapsY[0]?.offset ?? 0,
];
// Clear the min offset
minOffset[0] = 0;
minOffset[1] = 0;
nearestSnapsX.length = 0;
nearestSnapsY.length = 0;
const newDragOffset: [number, number] = [
round(dragOffset[0] + snapOffset[0]),
round(dragOffset[1] + snapOffset[1]),
];
// 2nd round, a new offset must be considered.
getPointSnaps(newDragOffset);
// Render snap linesGet gap snaps
Beyond the currently selected shape on the canvas, other shapes may form pairs with gaps between them. The diagram in the Excalidraw code illustrates this well—take horizontalGap as an example:
// https://github.com/excalidraw/excalidraw/blob/f55ecb96cc8db9a2417d48cd8077833c3822d64e/packages/excalidraw/snapping.ts#L65C1-L81C3
export type Gap = {
// start side ↓ length
// ┌───────────┐◄───────────────►
// │ │-----------------┌───────────┐
// │ start │ ↑ │ │
// │ element │ overlap │ end │
// │ │ ↓ │ element │
// └───────────┘-----------------│ │
// └───────────┘
// ↑ end side
startBounds: Bounds;
endBounds: Bounds;
startSide: [GlobalPoint, GlobalPoint];
endSide: [GlobalPoint, GlobalPoint];
overlap: InclusiveRange;
length: number;
};If the bounding box of the selected shape does not overlap with the gap, skip the detection.
for (const gap of horizontalGaps) {
if (!rangesOverlap([minY, maxY], gap.overlap)) {
continue;
}
}Detect the center point, right edge, and left edge in sequence:
// center
if (gapIsLargerThanSelection && Math.abs(centerOffset) <= minOffset[0]) {
}
// side right
if (Math.abs(sideOffsetRight) <= minOffset[0]) {
}
// side left
if (Math.abs(sideOffsetLeft) <= minOffset[0]) {
}If the condition is met, record it. During the process, continuously record the minimum distance:
const snap: GapSnap = {
type: 'gap',
direction: 'center_horizontal',
gap,
offset: centerOffset,
};
nearestSnapsX.push(snap);Render snap lines
Render snap lines in SVG container, see: Lesson 26 - Lasso selection.
Snap points are typically represented by a “cross,” and the lines connecting these points can be rendered using <line>.
renderSnapLines(
api: API,
snapLines: { type: string; points: [number, number][] }[],
) {
const { svgSVGElement } = this.selections.get(api.getCamera().__id);
this.clearSnapLines(api);
snapLines.forEach(({ type, points }) => {
if (type === 'points') {
const pointsInViewport = points.map((p) =>
api.canvas2Viewport({ x: p[0], y: p[1] }),
);
const line = createSVGElement('polyline') as SVGPolylineElement;
svgSVGElement.appendChild(line);
}
});
}Regarding the display of gap snap lines, Excalidraw's documentation is highly illustrative. Building upon this, we can add text labels indicating distance below auxiliary lines (horizontal direction) or to the right of them (vertical direction), similar to how Figma handles it:
// a horizontal gap snap line
// |–––––––||–––––––|
// ^ ^ ^ ^
// \ \ \ \
// (1) (2) (3) (4)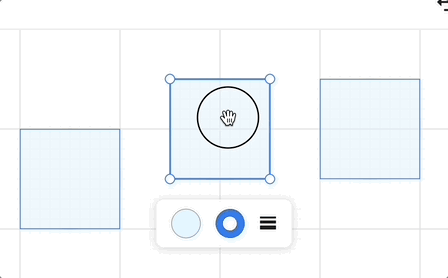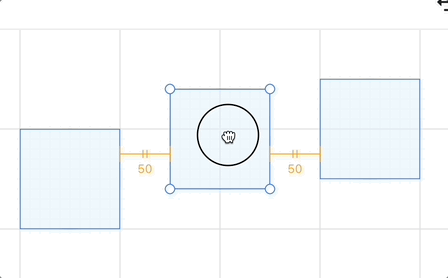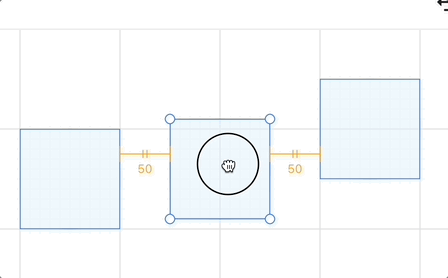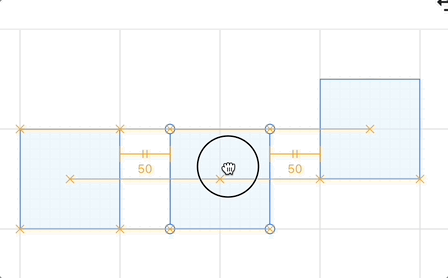
You can move the middle rectangle in the example below to experience the effect: