课程 22 - VectorNetwork
在这节课中你将学习到以下内容:
- SVG Path 的局限性
- 什么是 VectorNetwork?
- 使用 Pen 工具修改 Path
SVG Path 的局限性
在 课程 13 中我们学习了 Path 的绘制方式。Figma 也提供了 VectorPath API,它支持 SVG Path 的路径命令子集(详见:VectorPath-data)和 fillRule(Figma 中称作 windingRule)。
node.vectorPaths = [
{
windingRule: 'EVENODD',
data: 'M 0 100 L 100 100 L 50 0 Z',
},
];那为什么还要引入 VectorNetwork API 呢?原因在于 SVG Path 存在一些天然的局限性。The Engineering behind Figma's Vector Networks 一文很直观地展示了这一点。下面的图形是无法仅仅使用一个 Path 描述的:

只能通过拆分成多个 Path 描述,虽然可行,但在编辑场景下无法实现某些很符合直觉的操作。例如拖动左下的中心顶点时,只有一个顶点会跟随,因为它由两个独立的 Path 组成:

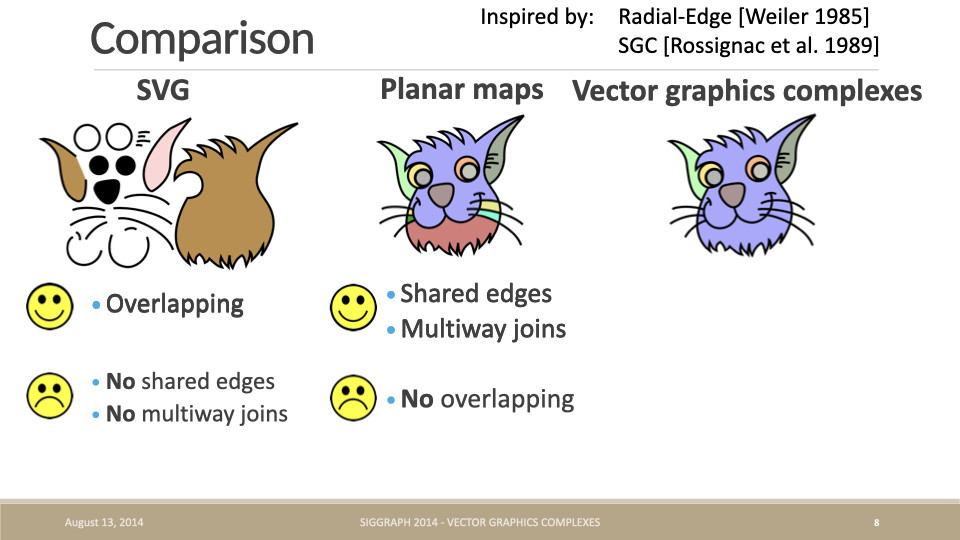
除了顶点无法拥有超过 2 条边,边也无法共享。Vector Graphics Complexes 的原始论文和 PPT 中对比了 SVG 和 Planar maps,两者都无法支持重叠、共享顶点和边这些特性,这才引出了一种新的几何表达(下文简称为 VGC):
vpaint 就是基于 VGC 实现的,可以看到完成合并点和边的操作之后,编辑中的联动效果是多么自然:
或者使用 The Engineering behind Figma's Vector Networks 一文中拖拽立方体一条边的例子:

值得一提的是,Discussion in HN 中提到了 VGC 和 Figma 的 VectorNetwork 之间奇妙的相似程度,考虑到两者几乎处于同一时期开始探索,在某种程度上算殊途同归,因此下文就使用 VectorNetwork 这一名词了。
CEO of Figma here. Most of the original insights around vector networks were in 2013, though we continued to polish the implementation over time. We didn't exit stealth and ship the closed beta of Figma until December 2015 which is why there isn't blog content before then. At first glance, this thesis looks super neat! I'm excited to check it out! I don't believe I've seen it before which is surprising given the overlap.
下面我们来看 VectorNetwork 是如何定义的。
VectorNetwork 的拓扑定义
VectorNetwork / VGC 的定义相比 Path 路径要复杂得多,其数据结构是一个图,由顶点、边和面(填充区域)组成,下图来自 Vector Graphics Complexes 原始论文。它不需要特定的方向或闭合于起始点,允许多个路径在同一对象内向任何方向分支,这使得创建复杂形状更加迅速高效。
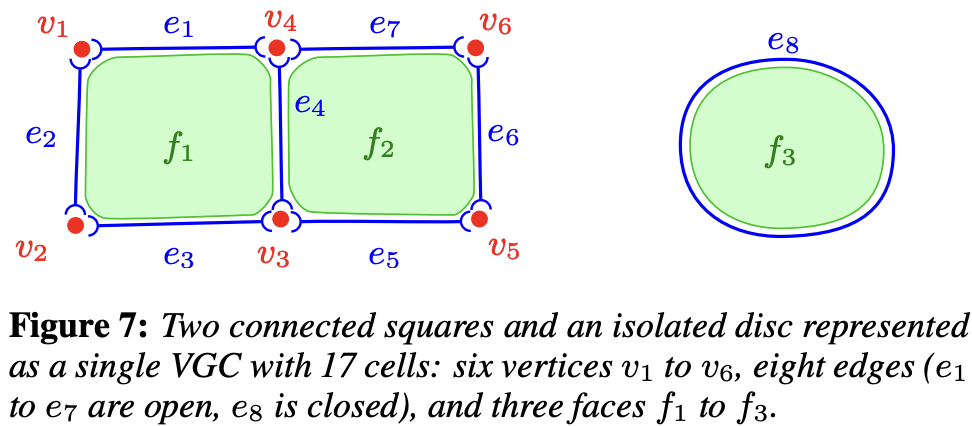
这里仅讨论拓扑定义,其他绘图属性和 Path 可以保持一致:
On top of this core structure, more drawing attributes can be added for fine control on rendering. For instance, we added vertex radius, variable edge width, cell color (possibly transparent), and edge junctions style (mitre join or bevel join).
顶点很好理解,在 VGC 中的边由一组 start 和 end 的顶点索引组成,两者重合时为自环。
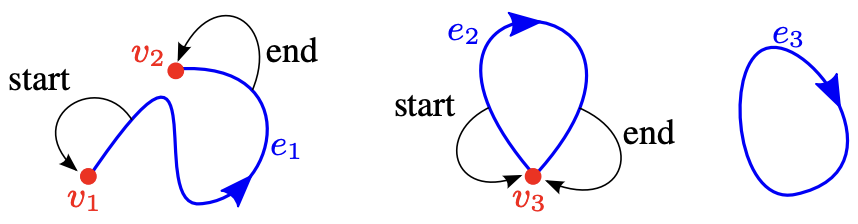
而填充区域由一组顶点组成的闭合环路定义。在 VGC 中使用一组 halfedge 定义:
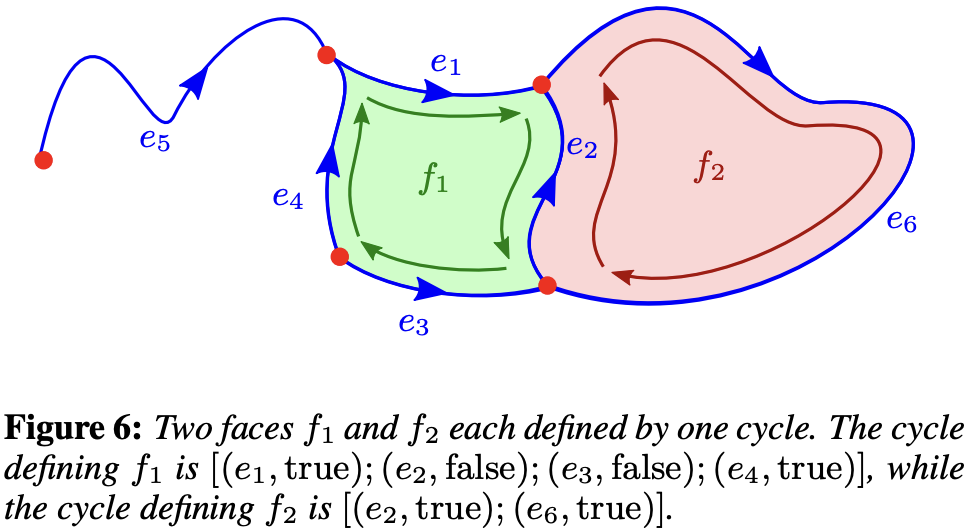
下面三角形的例子来自 VectorNetwork API,可以看到和 VGC 基本一致,只是填充区域由顶点索引和 fillRule 定义。其他非几何定义属性例如 strokeCap 和 Path 保持一致:
node.vectorNetwork = {
// The vertices of the triangle
vertices: [
{ x: 0, y: 100 },
{ x: 100, y: 100 },
{ x: 50, y: 0 },
],
// The edges of the triangle. 'start' and 'end' refer to indices in the vertices array.
segments: [
{
start: 0,
tangentStart: { x: 0, y: 0 }, // optional
end: 1,
tangentEnd: { x: 0, y: 0 }, // optional
},
{
start: 1,
end: 2,
},
{
start: 2,
end: 0,
},
],
// The loop that forms the triangle. Each loop is a
// sequence of indices into the segments array.
regions: [{ windingRule: 'NONZERO', loops: [[0, 1, 2]] }],
};在编辑场景下,顶点和边由用户定义,而填充区域需要系统自动计算。那如何找到这些填充区域呢?
Filling
在 click to fill 这样的操作中,需要找到顶点组成的最小环路。

转换方法
参考 figma-fill-rule-editor,我们给出如下类型定义:
export class VectorNetwork {
@field.object declare vertices: VectorVertex[];
@field.object declare segments: VectorSegment[];
@field.object declare regions?: VectorRegion[];
}
interface VectorVertex {
x: number;
y: number;
}
interface VectorSegment {
start: number;
end: number;
tangentStart?: VectorVertex;
tangentEnd?: VectorVertex;
}
interface VectorRegion {
fillRule: CanvasFillRule;
loops: ReadonlyArray<ReadonlyArray<number>>;
}Polyline 是最容易转换成 VectorNetwork 的图形:
class VectorNetwork {
static fromEntity(entity: Entity): VectorNetwork {
if (entity.has(Polyline)) {
const { points } = entity.read(Polyline);
const vertices: VectorVertex[] = points.map(([x, y]) => ({ x, y }));
const segments: VectorSegment[] = points.slice(1).map((_, i) => ({
start: i,
end: i + 1,
}));
return { vertices, segments };
}
}
}Bending
下文来自 Introducing Vector Networks - Bending,对于贝塞尔曲线的编辑,在 Path 和 VectorNetwork 中都是通用的:
Vector graphics today are based on cubic bezier splines, which are curves with two extra points called control handles that are positioned away from the curve itself and that control how much it bends, sort of like how a magnet might bend a wire towards it. Changing the shape of a curve involves dragging a control handle off in space instead of dragging the curve directly.

在 VectorNetwork 的边定义中,使用 tangentStart 和 tangentEnd 可以定义三阶贝塞尔曲线的两个控制点,当两者为 [0, 0] 时退化为直线。
也可以在 Konva 的 How to modify line points with anchors? 在线例子或者 bezierjs 中体验。
参考 Figma 的交互,在图形上双击进入 VectorNetwork 编辑状态,详见:Edit vector layers。
export enum Pen {
SELECT = 'select',
HAND = 'hand',
VECTOR_NETWORK = 'vector-network',
}有别于 课程 21 - Transformer 中基于 OBB 的实现:
- 拖拽 VectorSegment 和 OBB 一样,移动整个图形
- 拖拽 VectorVertex
Topological operators
Creation & delete
Delete and Heal for Vector Networks
Glue & unglue
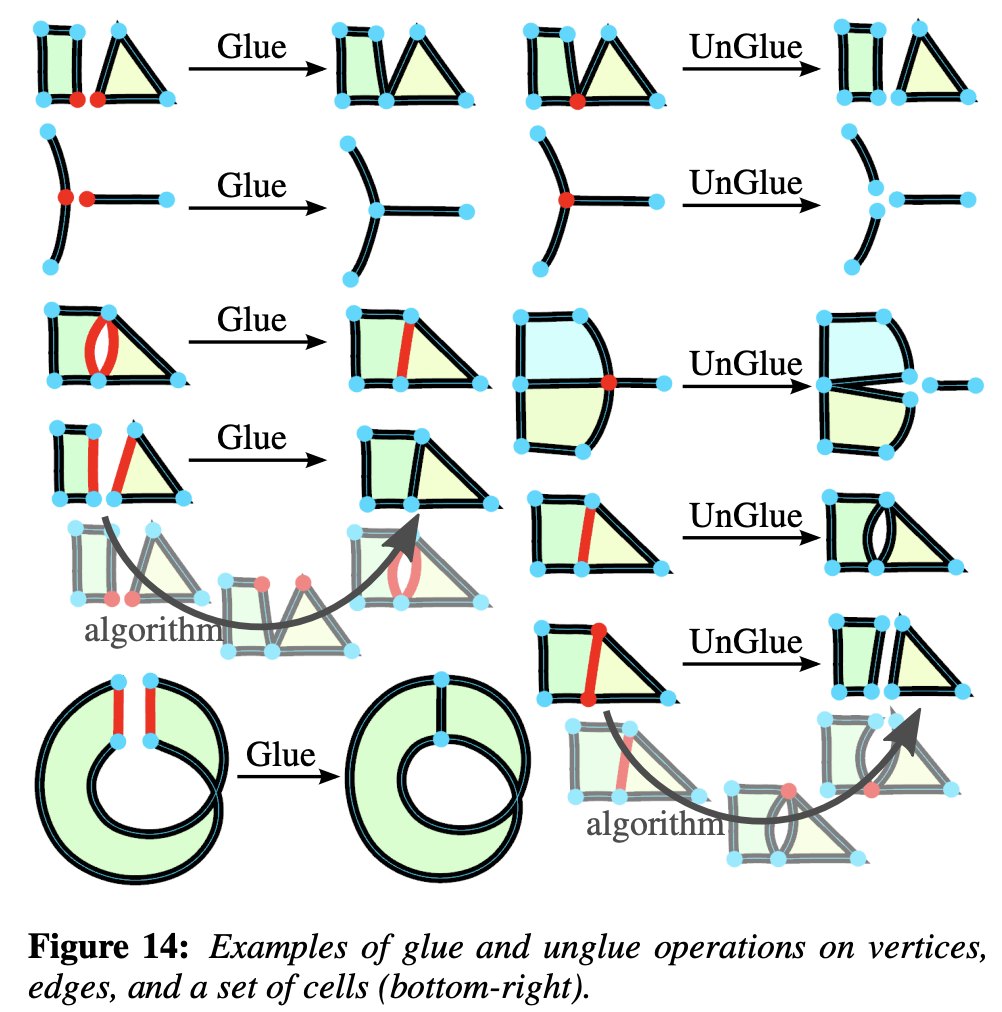
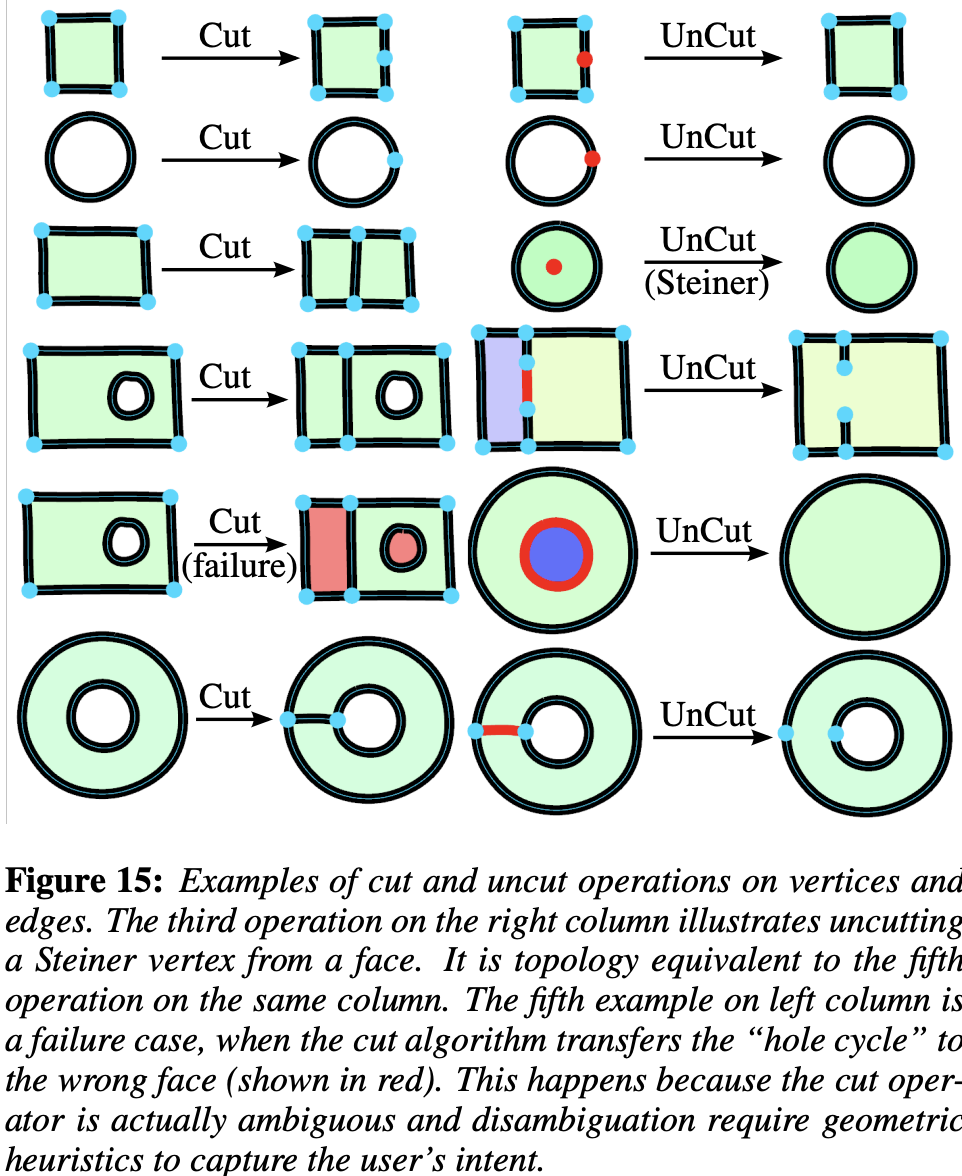
Cut & uncut